China Publishes Detailed Study of Coronavirus, over 12,000 People Recover

China’s health officials have published a detailed study about the COVID-19 epidemic in the country. The study details over 44,000 cases since the outbreak began in the paper published in the Chinese Journal of Epidemiology.
The study, titled ‘The Epidemiological Characteristics of an Outbreak of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Diseases (COVID-19) — China, 2020’, is available on the website of the CCDC (Chinese Centre for Disease Control and Prevention).
The paper looked into 44,672 confirmed cases of COVID-19 across China until February 11. Results in the study confirm previous description of the virus and patterns of infection
Out of the over 40,000 cases, 80.9% of the infections are classified as mild, 13.8% are found to be severe and 4.7% cases are critical. The fatality rate, which is the number of deaths among those infected, remains low, but it rises among those above over 80 years of age. Hubei province, which has Wuhan as its capital, is the most affected part in China. The fatality rate in this province is 2.9% as compared to 0.4% in the rest of the country. The overall fatality rate of COVID-19 has been found to be 2.3%.
The variation of fatality rates across different age groups has also been enumerated in the study. It stands at a low 0.2% for those till the age of 39 but gradually increases as the age goes up. The death rate is 0.4% for people in their 40s, 1.3% for those in their in 50s, 3.6% for those between 6 0 and 70 and rises to 8.0% for those in their 70s.
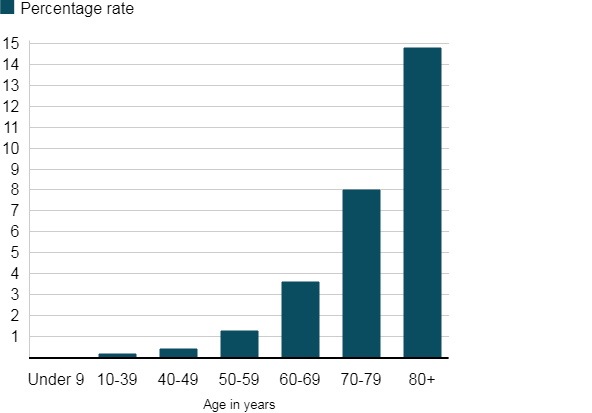
Coronavirus Fatality Rate in China. Image courtesy: Chinese Centre for Disease Control (CCDC).
In terms of gender, the study finds that men are more likely to die at a rate of 2.8% as compared to women who stand at 1.7%.
The study also considers which existing diseases put patients at more risk. It finds that cardiovascular diseases put a person at maximum risk of infection followed by diabetes, chronic respiratory disease and finally hypertension.
The study also assessed the risk to medical staff. It was found that a total of 3,019 health workers were infected, out of which 1,716 cases were confirmed. Five health workers died till February 11, the last day which had data included in the research. Fifty-one-year-old Liu Zhiming was the director of the Wuchang Hospital in Wuhan. He was one of the senior-most health officials to die of the COVID-19.
On February 17th, reports mentioned 98 new deaths due to the virus and 1,886 new cases. Out of the 98, 93 deaths and 1807 infections were reported from Hubei province, the epicenter of the epidemic.
However, the recovery rate offers cause for hope. A total of over 12,000 people have recovered, according to reports.
The epidemic curve, as the study finds, peaked between January 23 and had been declining till February 11. The downward trend, the study suggests is possibly due to the isolation of whole cities, high frequency broadcasting of critical information through multiple channels and deployment of multi-sector rapid response teams. The authors of the study also warn of a possible rebound of the epidemic with many people are returning from a long holiday.
Get the latest reports & analysis with people's perspective on Protests, movements & deep analytical videos, discussions of the current affairs in your Telegram app. Subscribe to NewsClick's Telegram channel & get Real-Time updates on stories, as they get published on our website.